ADVERTISEMENT
Definitions
General
The hyperbolic sine function is defined as:
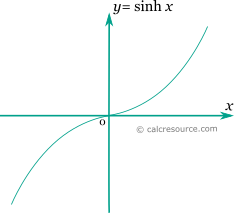
The graph of the hyperbolic sine function is shown in the figure below. It is a monotonic function unlike the trigonometric sine, which is periodic .
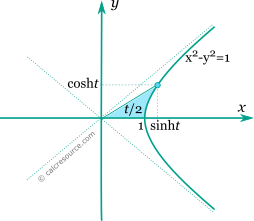
The points form the right wing of an equilateral hyperbola (see figure below), just like the trigonometric cosine, sine pairs form a circle. Parameter t is the half area between the hyperbola, the x-axis and a ray from origin to the point.
Series
All hyperbolic functions can be defined in an infinite series form. Hyperbolic sine function can be written as:
From the expanded form of the series it can be seen that the higher terms become insignificant, for values of x close to zero, resulting in the following quite useful approximation:
Properties
The derivative of the hyperbolic sine function is the hyperbolic cosine:
The integral of the hyperbolic sine is given by:
