Properties of Tetrahedron
This tool calculates the basic geometric properties of a regular tetrahedron. Choose the known characteristic of the object and enter the appropriate value for it. The calculated results will have the same units as your input. Please use consistent units for any input.
Known data: | |||
Geometric properties: | |||
Volume = | |||
Surface area = | |||
Face area = | |||
Edge length a = | |||
Height h = | |||
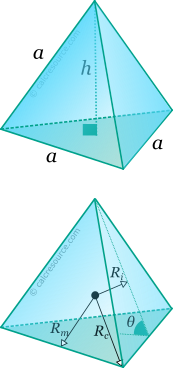
Inradius Ri = | |||
Circumradius Rc = | |||
Midradius Rm = | |||
Dihedral angle θ(°) = | |||
Number of faces = | |||
Number of edges = | |||
Number of vertices = | |||
 |
ADVERTISEMENT
Definitions
Geometry
Tetrahedron is a regular polyhedron with four faces. By regular is meant that all faces are identical regular polygons (equilateral triangles for the tetrahedron). It is one of the five platonic solids (the other ones are cube, octahedron, dodecahedron and icosahedron). It has 4 faces, 6 edges and 4 vertices and has the form of a pyramid with triangular base.
The volume of a tetrahedron is given by the formula:
where the area of one face and the height of the pyramid, that is the distance from one vertex towards the opposite face centroid. Both quantities can be expressed as functions of the edge length :
Therefore, volume can be expressed, as a function of side length , as:
The total surface area is given by the following formula:
The dihedral angle is defined as the interior angle between two adjacent faces of the polyhedron. For the regular tetrahedron it is given through the expression:
For any regular polyhedron, three spheres can be commonly defined: one that passes through all the vertices, called circumscribed sphere or circumsphere, one that passes through the centroids of all faces, called inscribed sphere or insphere, and one that passes through the middles of all edges, called midsphere. The radii of these spheres, circumradius , inradius and midradius , respectively, can be found for a regular tetrahedron, through the following expressions: